Dementia affects over 55 million people around the world, with women being more impacted than men. It is the seventh leading cause of death globally, and Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form. While dementia can take many forms, the life expectancy after a diagnosis can vary based on factors like age and the specific type of dementia. Most people diagnosed later in life, particularly after 70 or 80, tend to have a shorter dementia life expectancy over 80.
This blog will explore the different types of dementia, the impact on life expectancy, and ways to improve quality of life following a diagnosis.
What is the life expectancy for someone with vascular dementia?
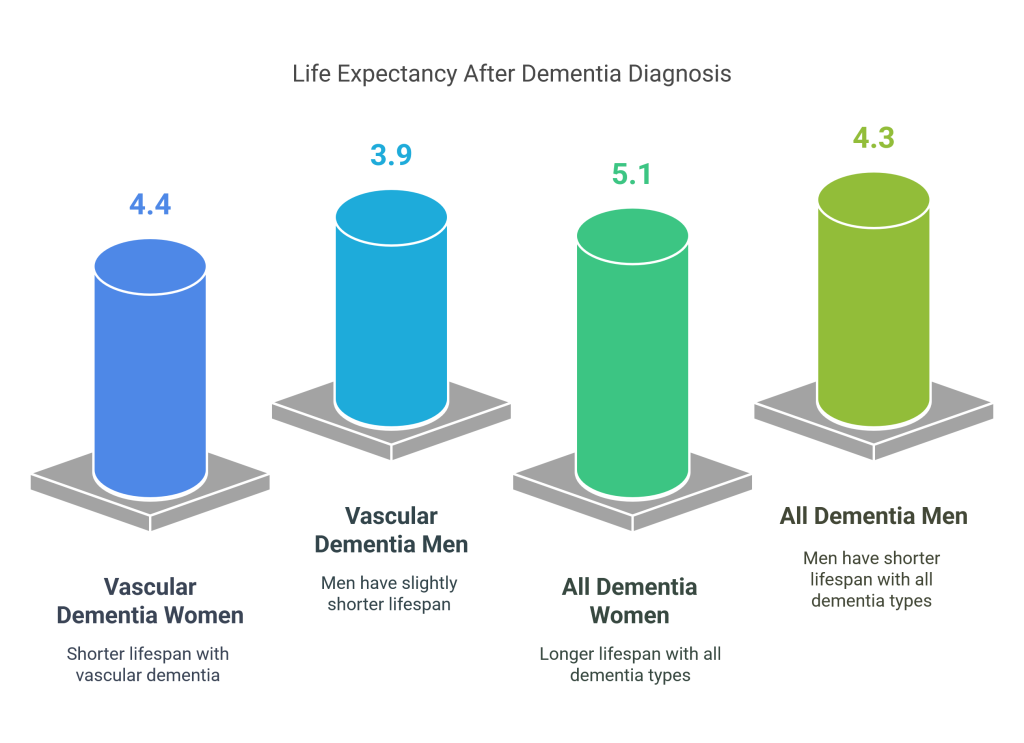
National Institutes of Health found that the average life expectancy after being diagnosed with vascular dementia is:
- 4.4 years for women
- 3.9 years for men
The same study showed that the average life expectancy for all types of dementia is:
- 5.1 years for women
- 4.3 years for men
All types of dementia shorten life expectancy. In general, life expectancy for vascular dementia is shorter than for Alzheimer’s disease, which is the most common type of dementia. However, everyone’s situation is different. The National Institutes of Health says that some people may live many years with the condition or may pass away from another cause, particularly when considering dementia life expectancy over 80.
How Dementia Affects Older Adults?
While some memory changes are expected as we age, dementia is not part of normal aging. However, getting older is the most significant known risk for developing dementia.
This happens because of changes in the brain as people age. About 3% of people aged 70 to 74 are diagnosed with dementia, but this increases to 22% for those between 85 and 89 and 33% for those over 90.
It’s normal to occasionally forget where you placed your keys or the name of someone you just met. What is not normal is forgetting things you used to rely on daily, like the knowledge needed for your job, language, or influential memories. The common symptoms of dementia can include:
- Taking longer or needing help to easily do simple tasks you used to do.
- Forgetting the names of people, what things are called, and what their purpose is.
- Misplacing items or getting lost.
Certain lifestyle factors, like being socially isolated and the design of the community you live in, are linked to dementia in older adults. If you are wondering which is worse—Dementia or Alzheimer’s Disease, read this post to know more about it.
What are the risk factors of Vascular Dementia Life Expectancy Over 80?
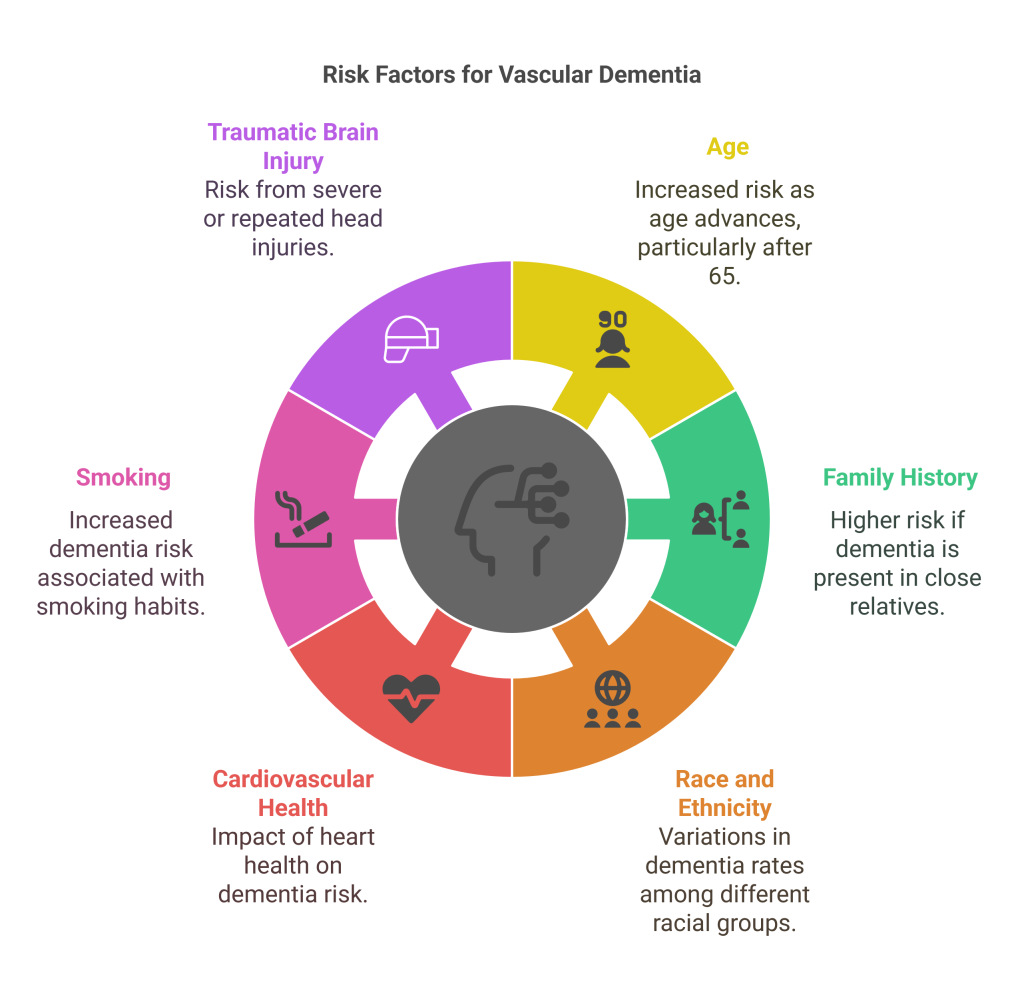
While healthcare experts do not understand what causes dementia, they believe it is likely due to a mix of brain changes from aging, along with genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. There are several risk factors for dementia:
- Age: Dementia usually affects people aged 65 and older. Age is the most substantial risk factor.
- Family History: Dementia can run in families. If a close family member, like a parent or sibling, has dementia, your risk may be higher.
- Race and Ethnicity: Black and Hispanic populations tend to have higher rates of dementia than Caucasians.
- Cardiovascular Health: Poorly controlled high blood pressure and high cholesterol can increase the risk of dementia.
- Smoking: Smoking raises the risk of developing dementia.
- Traumatic Brain Injury: A severe head injury or repeated head injuries can increase the risk.
It can also take time for symptoms to show up. Some believe the brain changes that lead to Alzheimer’s symptoms begin more than a decade before they are noticeable.
Top Factors That Affect Life Expectancy Over 80
Taking care of your mental and physical health is important in the early stages of dementia. This includes eating well, exercising, staying social, getting enough sleep, and being mindful.
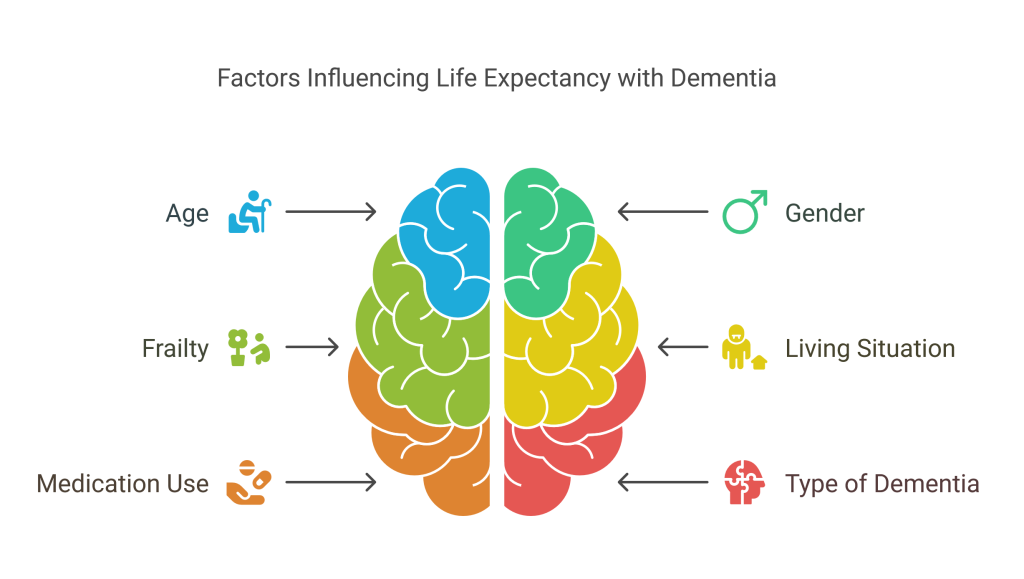
Several factors can affect how long someone lives after being diagnosed with dementia.
Other factors that may shorten life expectancy include:
- Being older
- Being male
- Frailty
- Living alone
- Taking five or more prescription medications
- Certain types of dementia, like Parkinson-Plus Syndrome (PPS) or dementia, are caused by multiple factors.
Age and male gender are the most consistent factors that can lower life expectancy after a dementia diagnosis. Although you cannot change these factors, you can still improve your quality of life, even considering dementia life expectancy is over 80.
How to Improve Your Quality of Life?
When someone is diagnosed with dementia, care suggestions include:
- By offering complete care that looks at other health problems, they may have along with dementia, people with dementia may have trouble taking care of themselves and managing other health issues. Mental health care and social support are also critical.
- Managing the person’s mental health symptoms and understanding that certain medications may not work well and could even be harmful to people with dementia.
- Supporting family members can reduce the stress of caregiving and improve the patient’s quality of life.
- The ability of a person with dementia to keep their social relationships can also make a big difference. Patients should talk to their doctor or a therapist for advice on handling social situations.
Also, keeping up with household tasks for as long as possible can improve the quality of life and help prevent the person from becoming too inactive. In later stages, a person’s needs may change, and caregivers should know how to care for themselves and their loved ones.
Even though there is no cure for dementia, living a healthy life can delay the disease’s onset or sometimes even prevent it. Once diagnosed, several actions can offer complete care for dementia. However, it’s important to remember that many people live with severe disability due to the disease’s progress. A 2020 study found that among more than 50,000 people over the age of 65 diagnosed with dementia, about 41% passed away within 10 years. On average, women lived a little over five years, and men about four years after diagnosis.
The Bottom Line
Dementia is a common condition in individuals aged 65 and older, though it is not a normal part of aging. While dementia cannot be entirely prevented, specific lifestyle changes can help delay its onset. Modifying habits such as quitting smoking, staying active, and managing chronic conditions like high blood pressure may reduce the risk of developing dementia.
If you seek communities for senior living in Gold Beach options, consider a residential assisted living or assisted living facility like Shore Pines Senior Living. The communities provide excellent support for individuals and families navigating dementia care.